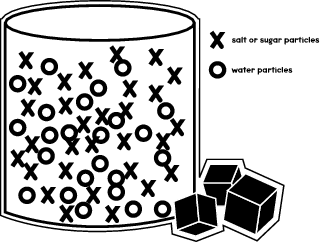
A The mass of the sugar and water is the same as the mass of the sugar solution B The mass of the sugar and water is greater than the mass of the sugar solution C The mass of the sugar solution is greater than the mass of the sugar and water D We do not have enough information to determine anything about the mass of the sugar, water, orThe lump gradually disappears as sugar molecules leave the surface of their crystals and mix with water molecules Eventually all the sugar molecules become uniformly dis tributed among the water molecules, as indicated by the equally sweet taste of any part of the mixtureAll visible traces of the solid sugar are SOLUTIONS395 SECTION131 In a beaker, sugar is dissolved in water, and then the water is heated and evaporates The sugar is recovered, and heat is again applied Vapor is released, and the material in the beaker changes from white to black What must

7 7 Solubility Chemistry Libretexts
A cup of sugar is slowly heated in a beaker which element will eventually remain in the beaker
A cup of sugar is slowly heated in a beaker which element will eventually remain in the beaker-Supersaturated add max amount of sugar to water, heat up, add more sugar, then cool down Explain why ethanol will dissolve in water and carbon tetrachloride will not ethanol is charged and has Hbonding like water, whereas tetrachloride has no charge and has dispersion forces I wanted to tell them that the sugar disappeared because it dissolved Obviously, all of us know that when sugar is mixed in water, it quickly disappears after stirring the liquid for a moment or two The question cannot be completely answered just by saying "because it dissolves", along with an eye roll and a shrug



Aheia Com Files 1160 Aheia Sausage Making Workbook Pdf
Glucose is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water The electrons release large amounts of energy each time they are transferred from one electron acceptor to another Oxygen is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water sugar melts when heated because the force of attraction between the atoms or molecules of sugar become weak and gradually break as more heat is applied to it and soon the sugar melts to become Furthermore distilled water mixed with iodine will be placed in a beaker, outside the dialysis bag After allowing some time to pass, the solution inside the dialysis tubing and the solution in the beaker will be tested for the presence of glucose and starch The presence of glucose will be determined with indicator strips
The water will remain the same temperature, but the metal will cool to 10°C The water and metal will adjust to the same temperature between 10°C and 1°C (08) A pot of cold water was heated on a stove until the water boiledHeat is energy that is transferred from a hotter to a cooler object Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold a substance feels Heat (energy transfer) occurs in three ways conduction, convection or radiation During conduction, the objects must be touching each other for energy transfer toExplain Science In the simulation shown below, each insulated beaker contains equal amounts of the same fluidThe starting temperature of beaker A was 1000 °C and the starting temperature of beaker B was 00 °C Assuming no heat is lost, what
ß Half fill a beaker with water (to act as a water bath) and put it on the hot plate to heat to 37C Check the temperature of the water regularly and adjust the hot plate so that the temperature stays as close to 37C as possible (alternatively turn on the incubator and set to 37C)Example 1 Above is illustrated an example of a saturated solutionIn Figure 1113, there is a constant amount of water in all the beakers Figure 11 shows the start of the saturation process, in which the solid solute begins to dissolve (represented by red arrows)In the next beaker, Figure 12, much of the solid solute has dissolved, but not2 b) A second student is given two solution, 750mL of 100M HCl and 750mL of 100M NaOH, each at 250°C The student pours the solutions into an insulated cup, stirs the mixture, covers the cup, and records the maximum temperature of the mixture i) The student calculates the amount of heat evolved in the experiment to be 411kJ




A Guide To Preparation Protocols In Palynology



Aheia Com Files 1160 Aheia Sausage Making Workbook Pdf
A) The metal exhibits an endothermic change b) The final temperature of the metal and the water will be the same c) Water exhibits an endothermic change d) Heat flows from the metal to the waterSome sympathetic inks appear and disappear again based on humidity To try one of these, make a solution of 1/8 teaspoon cobalt chloride and 1/2 cup water After writing your message and letting it dry, heat For the low temperature bath, use a 250mL or 400mL beaker, fill it about halfway with tap water, and add some ice to the water The temperature of this bath when it comes to constant temperature should be between 0 and 5°C To make the high temperature water bath, fill a 250mL or 400mL beaker about twothirds full and heat it until it boils



Science Projects For Beginners Chemistry



Energy Changes In Chemical Reactions
When sugar is heated to the point of darkening, it said to be caramelized Caramelization starts with a chemical break down of sugar (sucrose) into the two sugars that make it (fructose and glucose)Sugar or sucrose as it is scientifically termed when slowly heated melts to form liquid and when heating continues one or two things might happen to it Either it may spontaneously decomposes into decomposition products or it may caramelise If we When sugar is placed in a pot or pan over a flame or another source of heat, it transforms from a solid to a liquid substance It develops a different taste and smell, and the most common term for the result of heated sugar is caramel The molecules in heated sugar break down and produce several different compounds



Bnc British National Corpus Frequency Word List




Ch104 Chapter 7 Solutions Chemistry
A student was asked to prepare a true solution of sugar in water By chance, he added sugar in excess He stirred for quite some time but some of it settled down He filtered the contents The filtrate will be (a) true solution (c) suspension (Board Term 1, 12 Set0) (b) colloidal solution (d) can be true solution or colloidal solution QThe heat will make your secret writing appear! If they are placed in a sealed chamber, the lower vapor pressure of water in the glucose solution results in a net transfer of water from the beaker containing pure water to the beaker containing the glucose solution (bottom) Eventually, all of the water is transferred to the beaker that has the glucose solution




7 7 Solubility Chemistry Libretexts



Www Sidestone Com Openaccess Pdf
Squirt 4–5 drops of yellow food coloring into another small cup for each group Add ice to about 6 cups of tap water to make it sufficiently cold Pour about ¾ cup of cold water (no ice) into a cup for each group Pour about ¾ cup of hot water into a cup for each group Materials for each group Hot water (about 50 °C) in a clear plastic cupChemistry Demos Demos can be searched by keywords, title, or category number A light bulb will glow when a substance that conducts electricity is inserted in a break in the wires that leads to and from the power source Solutions that contain ionic compounds conduct electricity In a beaker, sugar is dissolved in water, and then the water is heated and evaporates The sugar is recovered, and heat is again applied Vapor is released, and the material in the beaker changes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__serious_eats__drinks.seriouseats.com__images__20110621shrub2-d48fad4bf61d4636abd40c055c379f39.jpg)



Cocktail 101 How To Make Shrub Syrups



Lab 4 Chemical And Physical Changes
Atoms of an element on one side of the equation has to match the number of atoms of that element on the other side A mole is a unit of measurement just like a "dozen" eggs is 12 eggs A mole, which was chosen because it is the number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon, is known as Avogadro's A hot metal cylinder is placed in water at room temperature in a closed system Which statement is NOT true concerning heat flow?4 Wearing white gloves, slip the beaker into the ring clamp and tightly clamp the beaker onto the extractor If the clamp is too loose, insert another gasket inside the ring 5 Raise the heaters into position Leave about a 1/4 inch gap between the beaker and the heating element 6



Q Tbn And9gctth8cj9tezqj3hgju1uuwc62hnd6tnqyt 6lhjrs7xqoeg1e0s Usqp Cau




Solids Liquids And Gases Particle Model Of Matter Siyavula
B Place the breaker with thermometer on a heater plate, turn on the heat until the water is boiling, and measure the temperature of boiling water c In a similar manner, find the boiling point of the salt water by replacing the water in the beaker with 100 mL of 10% solution (10 g of salt dissolved in 100ml of water) 334d Chapter 1 Chemical Foundations Classification and Separation of Matter Match each description below with the following microscopic pictures More than one picture may fit each description A picture may be used more than once or not used at all i ii iii iv v vi a a gaseous compound b aSugar, like all other substances, has a limit to its solubility in water That is why we cannot dissolve more than a particular quantity of sugar in a given volume of water Any sugar added after



1




The Two Beakers Below Each Have Added To Them The Chegg Com
Play this game to review Science Number 2 represents a _____ With Super, get unlimited access to this resource and over 100,000 other Super resourcesIt was more focused towards Beaker 2 This could be related to less accuracy of following results The thermometer showed that in Part II, Beaker 1 with greenhouse gasses warmed slower than Beaker 2 Hence, Beaker 1 also cooled slower thanAnswer choices stirring some sugar in water until you cannot see the sugar heating a pan of water until the water is all gone heating a block of ice until the ice turns to water cooling water in the freezer until the water becomes solid stirring some sugar in water until you cannot see the sugar




General Chemistry Chemistry




45 C Refer To The Two Beakers For Question 7 7 The Chegg Com
Get an answer for 'In a beaker, sugar is dissolved in water, and then the water is heated and evaporates The sugar is recovered, and heat is again applied Vapor isHeat is the transfer of energy from a substance at a higher temperature to a substance at a lower temperature Some materials are better conductors of heat than others Summary Students will do an activity in which heat is transferred from hot water to metal washers and then from hot metal washers to waterMix 1/3 cup of water and 1/3 cup of Elmer's glue together in a beaker or cup 2 Add a few drops of your favorite food coloring and mix 3 Make a solution of Borax by measuring 1/3 cup of water, and add Borax slowly with stirring until no more Borax will dissolve, and just a few grains of the solid remain on the bottom of the container 4




Sugar Science Fair Project Help Your Kids Do This



A Description Of Matter
Using the marker and masking tape label two cups for each compound "table salt," "table sugar," "baking soda" and "Epsom salts" Into one table salt cup measure 50 grams of saltSugar is made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms When heated over a candle, these elements react with the fire to turn into a liquid The heat causes the sugar's atoms to combine with the oxygen in the air, forming new groups of atoms Energy is released in this chemical reaction in the form of smoke and black soot Example 1 Saturated Solution;



Www Sidestone Com Openaccess Pdf



Www Moorparkcollege Edu Sites Moorparkcollege Files Media Pdf Document Chem 12 All Expts Pdf
When Part II ended, one cardinal problem was noticed The lamp which provided the light was defective;Diffusion results in the gradual mixing of materials, and eventually, it forms a homogeneous mixture Diffusion Particles in a liquidfilled beaker are initially concentrated in one area, but diffuse from their area of high concentration to the areas of low concentration until they are distributed evenly throughout the liquidUse a small, light blue flame to gently heat the contents of the beaker Continue gentle heating until the reaction is complete Aggressive heating will cause the contents to spatter out of the beaker in a violent manner You should periodically remove the Bunsen burner from beneath the beaker to slow the heating process




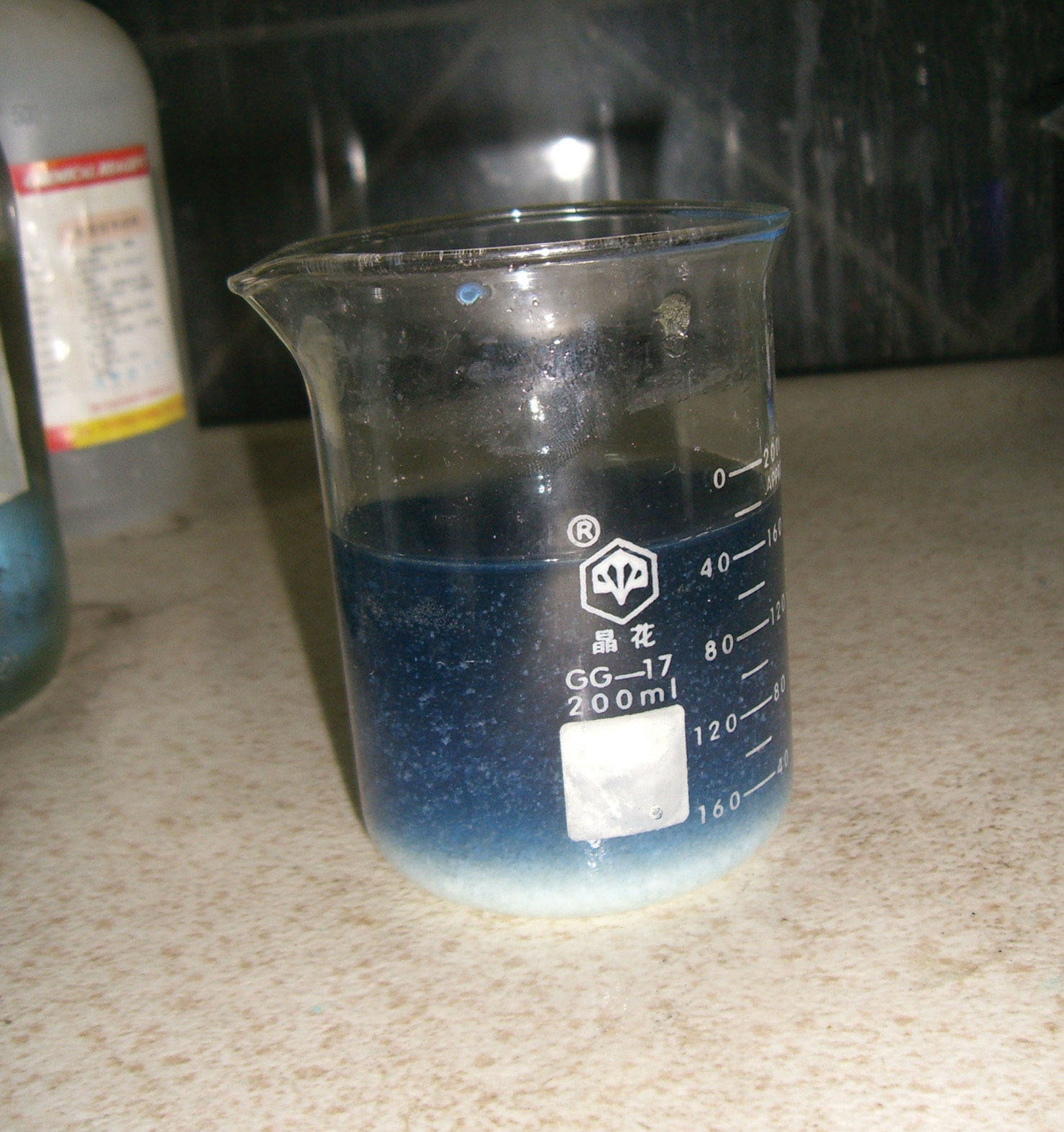
Evaporation Filtration And Crystallisation Cpd Rsc Education



Mixing Sugar And Water Assessments Of Argumentation In Science Stanford University
Eventually, only the salt crystals are left behind For example, we dissolve sugar (solute) in a cup of coffee (solvent) to drink Water Wire gauze in Porcelain chips Heat Beaker Figure 621 1 Pour the mixture of water and alcohol into the roundbottom flask until it is half full and add in some porcelain chips15 Questions Show answers Question 1 SURVEY 60 seconds Q A crystal of purple potassium manganate (VII) was added to each of the beakers shown in the diagram One beaker contained hot water and the other beaker contained cold water In both beakers the purple colour of the potassium manganate (VII) spreads out A student adds 5 g each of sand, sugar, and salt to 50mL of water Did he make a solution?




Unit 4 Test Review Ppt Download



Lab 4 Chemical And Physical Changes
• Pour the water into the beaker with the sodium acetate • Place the beaker on a hot plate and gently heat with stirring until all the sodium acetate is dissolved and you have a clear solution Note any observations • Gently remove the beaker from the hot place and leave to cool without disturbing the beaker The sugar cube would eventually dissolve because random motions of the water molecules would bring enough fresh solvent into contact with the sugar, but the process would take much longer It is important to realize that neither stirring nor breaking up a solute affect the overall amount of solute that dissolves The latent heat of freezing for water is about 80 cal/gm, enough to heat water 80°C So after 12/80 or 15% of your water froze, the temperature should have risen to 0° C and freezing should have slowed dramatically, requiring gradual heat leakage to the outside



Chemistry For Rwandan Schools Senior One Student S Book Mujuni Patrick Musisi Ronald Omutiti Peter Pdf Free Download



Science Form 1 Flip Ebook Pages 151 0 Anyflip Anyflip
Place the beaker of water on wire mesh (which should be on the ring) Gently heat the beaker of water until it is boiling As one person monitors the Bunsen burner, another needs to get 2 cups of sugar Once the water is boiling, slowly add one cup of the sugarA sugar cube is placed in a beaker containing water The beaker is left until the sugar cube disappears and a sugar solution forms The concentration of the solution is the same at the bottom and top of the beaker (a) Use the particle theory to explain what happens to the sugar cube to make the concentration of the solution the same at



Chemistry For Rwandan Schools Senior One Student S Book Mujuni Patrick Musisi Ronald Omutiti Peter Pdf Free Download




Petroleum Wikipedia



Ch104 Chapter 7 Solutions Chemistry




Mixtures Separating Mixtures Siyavula




X1v Heating Beakers Pt William Carlton Library Formative




Observation Pisscience




Lab Safety Chemistry Ppt Download



Www Acs Org Content Dam Acsorg About Governance Committees Chemicalsafety Publications Safety In Academic Chemistry Laboratories Students Pdf



Archive Ouverte Unige Ch Unige Attachment01
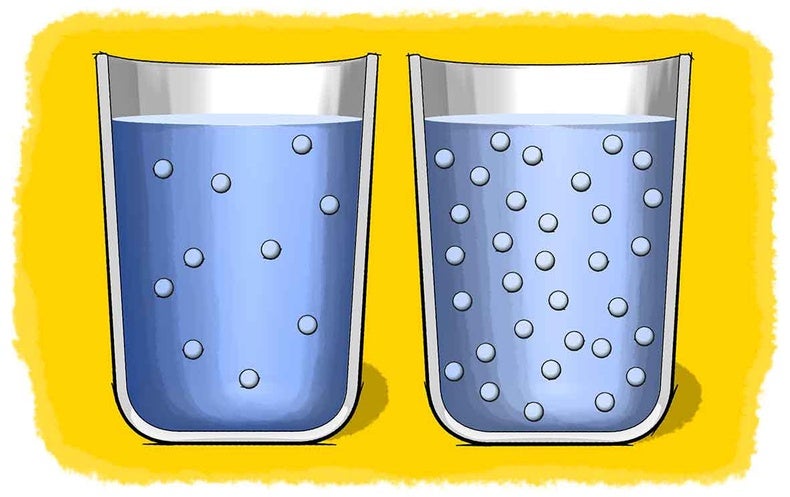



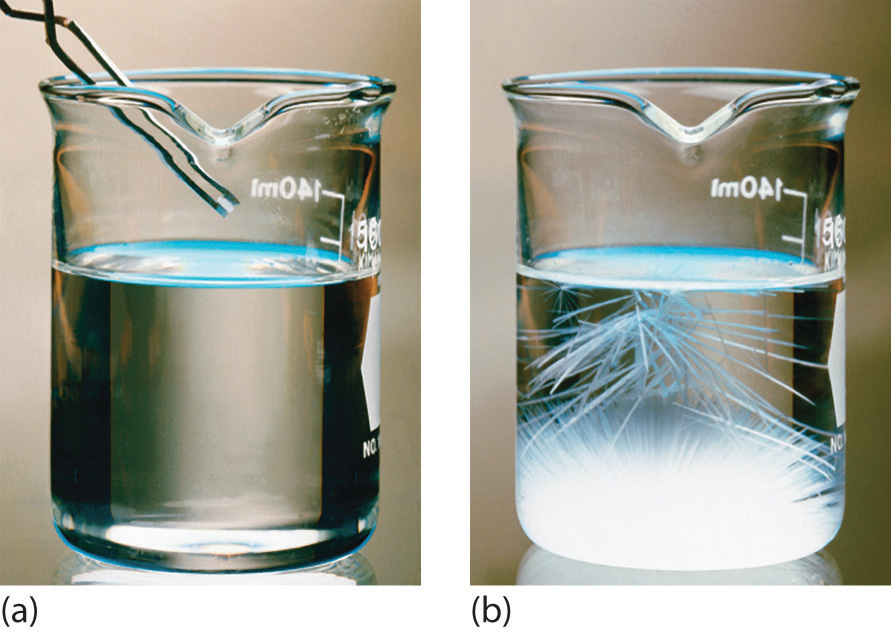
Solubility Science How Much Is Too Much Scientific American



Web Ung Edu Media Chemistry2 Chemistry Lr Pdf




Chemistry Igcse Text Book




9 Look At The Beakers Below An Which Beaker Would Sugardissolve Faster And Why Cold Brainly In




Convection Heat Energy Transfer Siyavula




Chemistry Notes Form 1 Chemistry Form One Pdf Online Notes Chem



2




Changes Of State Particle Model Of Matter Siyavula



Www Redlandsusd Net Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid Dataid 955 Filename Chapter 18 Chemical equilibrium Pdf



Lab 4 Chemical And Physical Changes



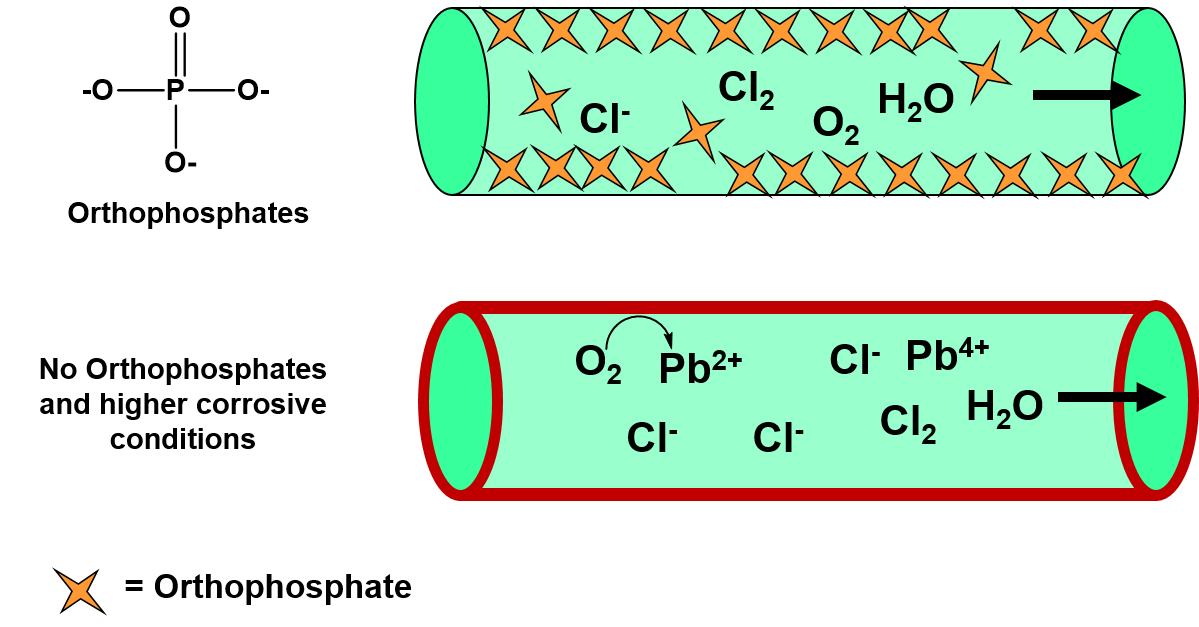
Ch103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis And Cellular Function Chemistry




8th Grade Review Powerpoint




Usa1 Method Of Preparing Tissues For Vitrification Google Patents




Pdf A Formal Characterisation Of Ceramics In Galician Bell Beaker Contexts



Color Change Chemical Reaction Experiments Hst




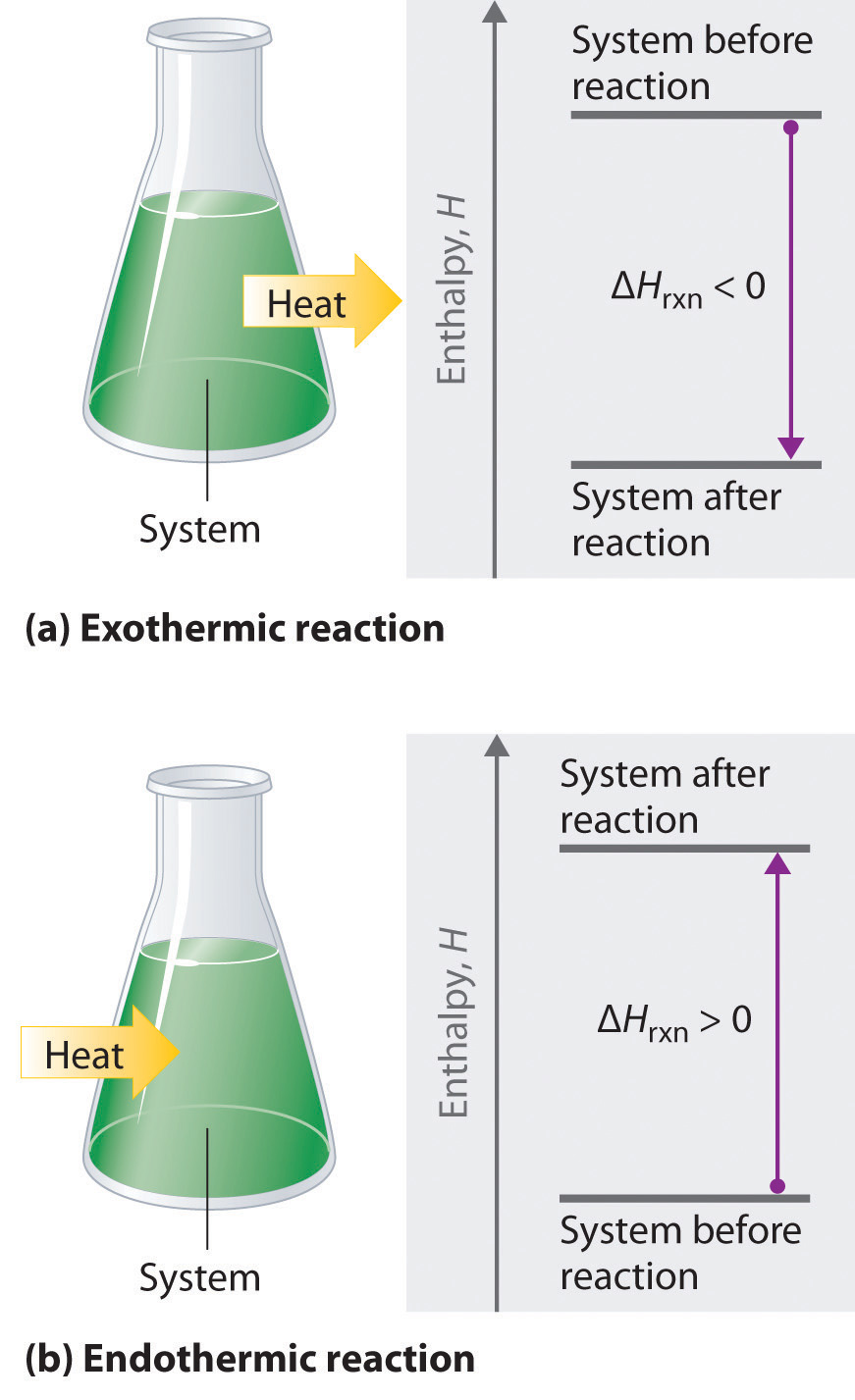
Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Pearson Canada
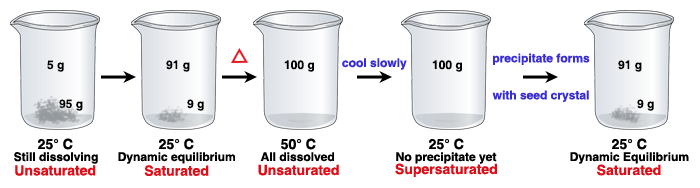



Types Of Solutions Saturated Supersaturated Or Unsaturated Texas Gateway




Calcium Oxyhydroxide Cao Ca Oh 2 Nanoparticles Synthesis Characterization And Evaluation Of Their Capacity To Degrade Glyphosate Based Herbicides Gbh Sciencedirect
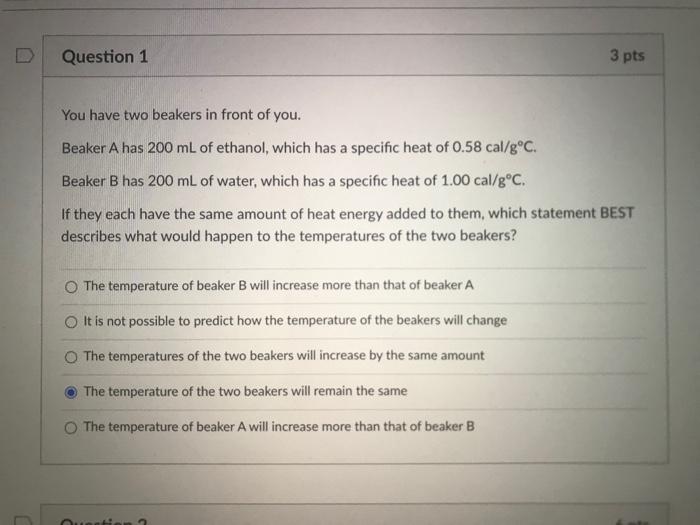



Solved Question 1 3 Pts You Have Two Beakers In Front Of Chegg Com



1




Making A Yeast Starter The Electric Brewery




Chemistry In Focus Y12 Metallic Elements Chemical Substances




Usree1 Compositions For Manufacturing Fiber Reinforced Starch Bound Articles Having A Foamed Cellular Matrix Google Patents



Www Redlandsusd Net Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid Dataid Filename Mc chapter 10 States of matter Pdf



2



Www Apsacssectt Edu Pk Secretariat Downloads Cp D Tg 21 22 Science New secondary science tg 1 class 6 19 6 Pdf




The Mad Fermentationist Homebrewing Blog How To Homebrew All Grain Beer




The Image Below Shows 3 Beakers Beaker A Contains A Chegg Com




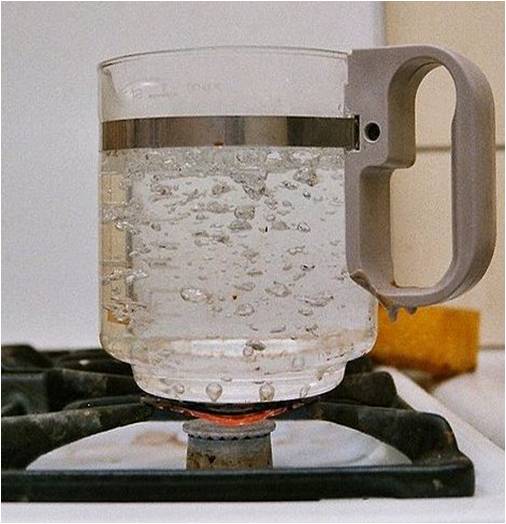
Chemical Reactions And Equations




Edexcel International Gcse 9 1 Chemistry Student Book Pdfdrive Com



Lab 4 Chemical And Physical Changes




Glass A Pocket Dictionary Of Terms Commonly Used Corning




Hydrochloric Acid Is Added To A Beaker Containing A Piece Of Zinc Ppt Download




Pdf Teaching Physical Concepts In Oceanography An Inquiry Based Approach




Scout Idea Bank By Scouting Ireland Issuu




Pdf A Formal Characterisation Of Ceramics In Galician Bell Beaker Contexts



Http Www Diva Portal Org Smash Get Diva2 Fulltext01 Pdf



Plainviewwater Org Wp Content Uploads 18 01 912introduction To Water Pdf




The Density Of A Substance Is Defined As Its Mass Per Unit Volume M V P Pdf Free Download




Chem 100 Lab Manual 21 Spring By Fgarces Issuu




Whs Proceedings By Murat Tasarsu Issuu




Igcse Summary Of Biology



Pes Skill Sheets Book Capital High School




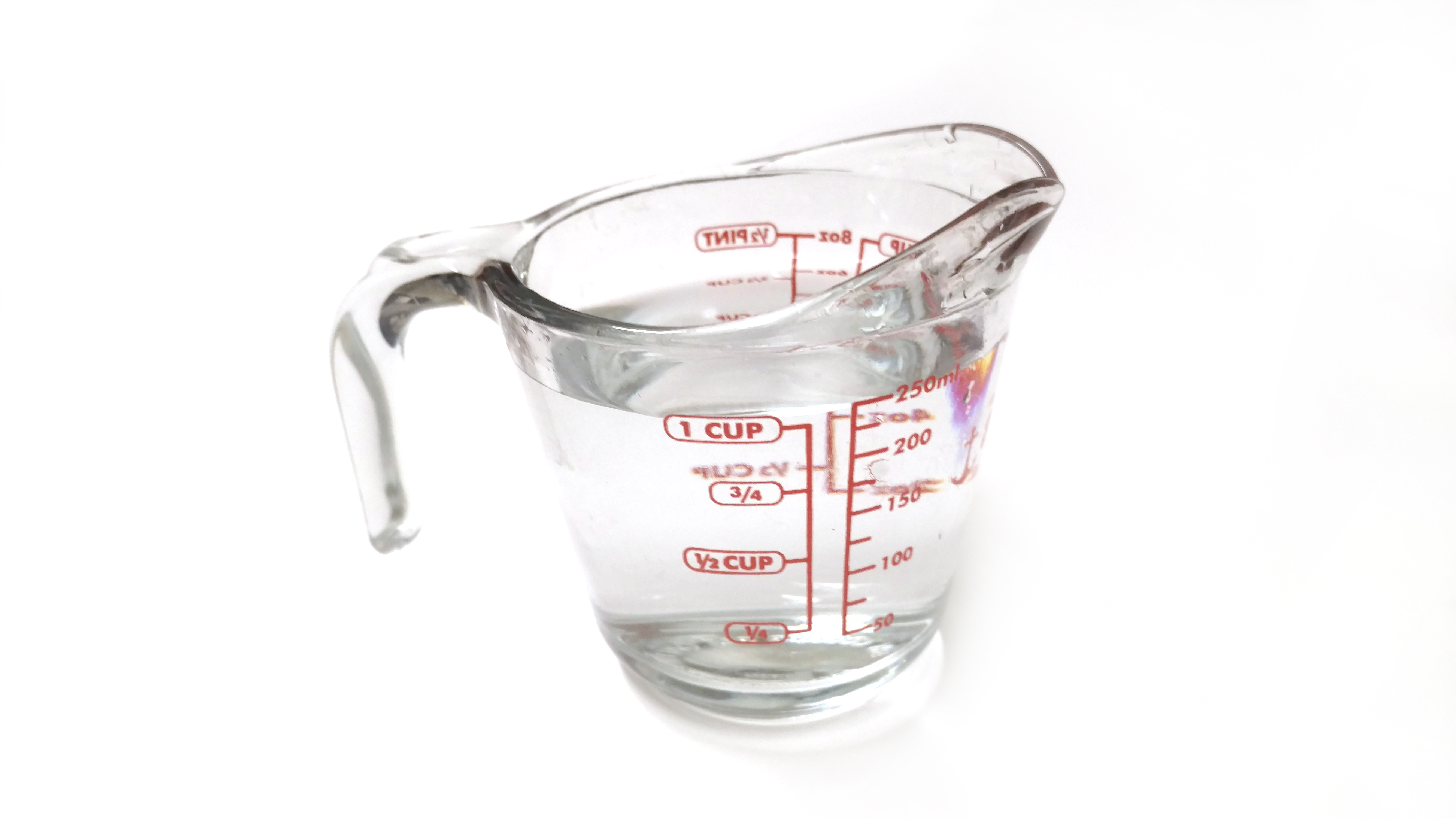
Boiling It Down To The Bubbles It Is About Heat Transfer A Lab Aloft International Space Station Research




Active Learning In Chemistry Education Chardon Local Schools



Lab 4 Chemical And Physical Changes



Science Form 1 Flip Ebook Pages 151 0 Anyflip Anyflip
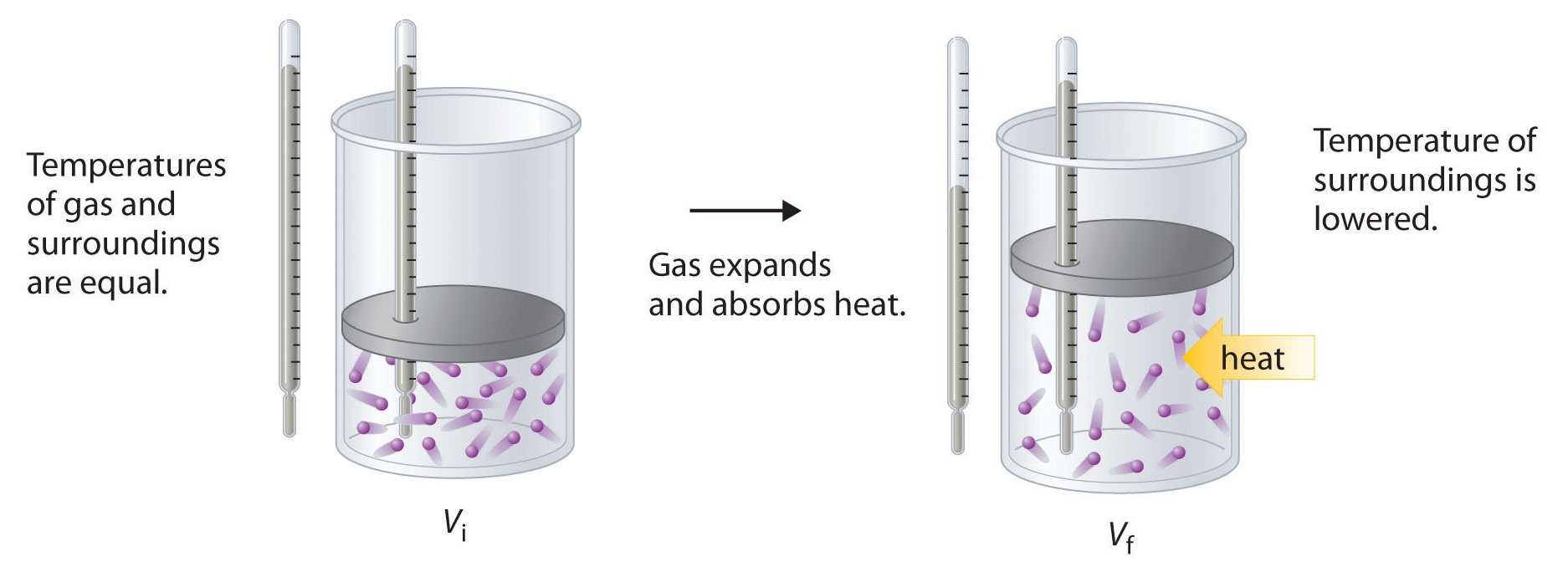



19 2 Entropy And The Second Law Of Thermodynamics Chemistry Libretexts
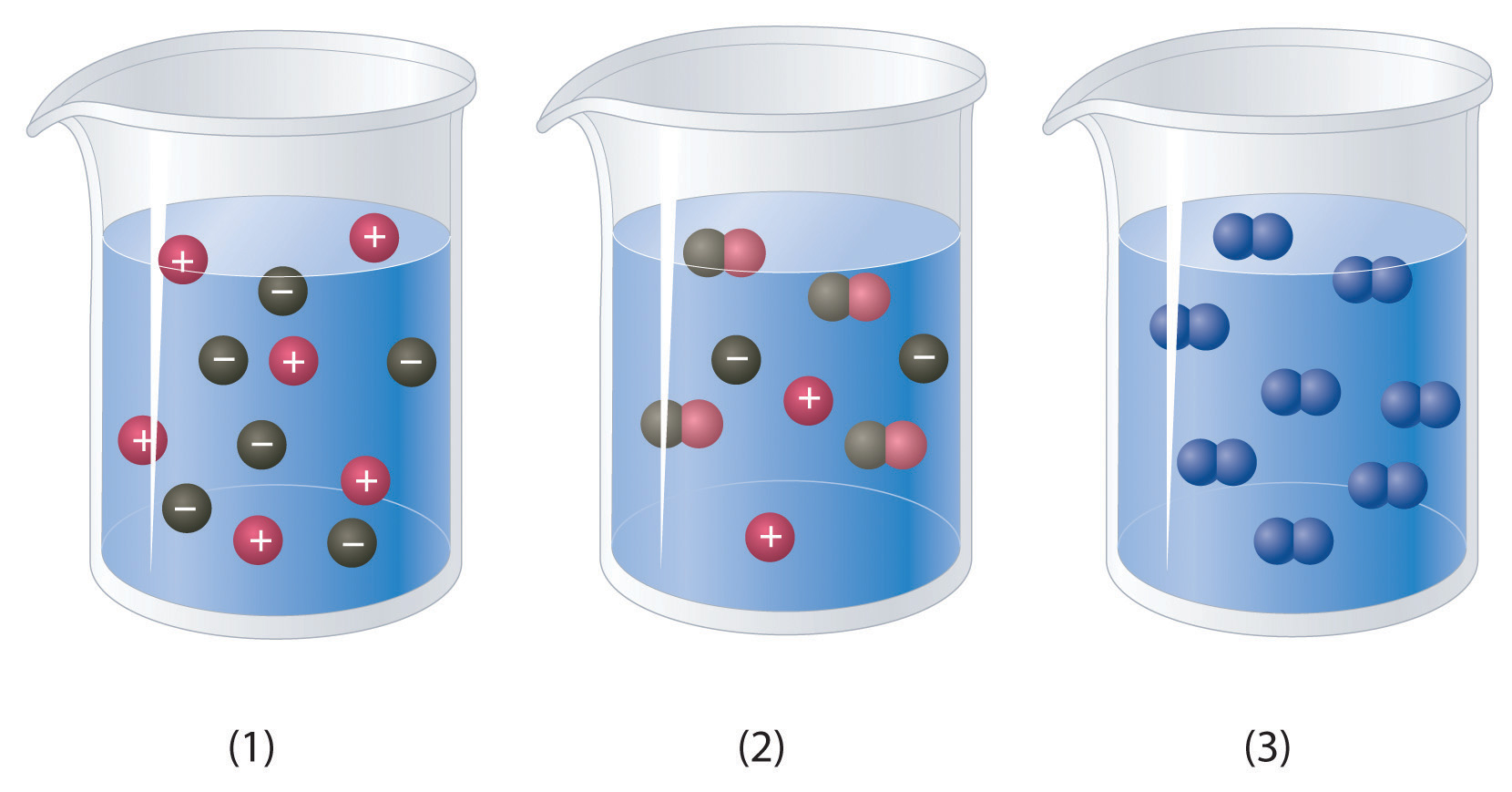



Ch104 Chapter 7 Solutions Chemistry



1



Www Northwestern Edu Open Educational Resources Docs Intro Chem Pdf



Mixing Sugar And Water Assessments Of Argumentation In Science Stanford University



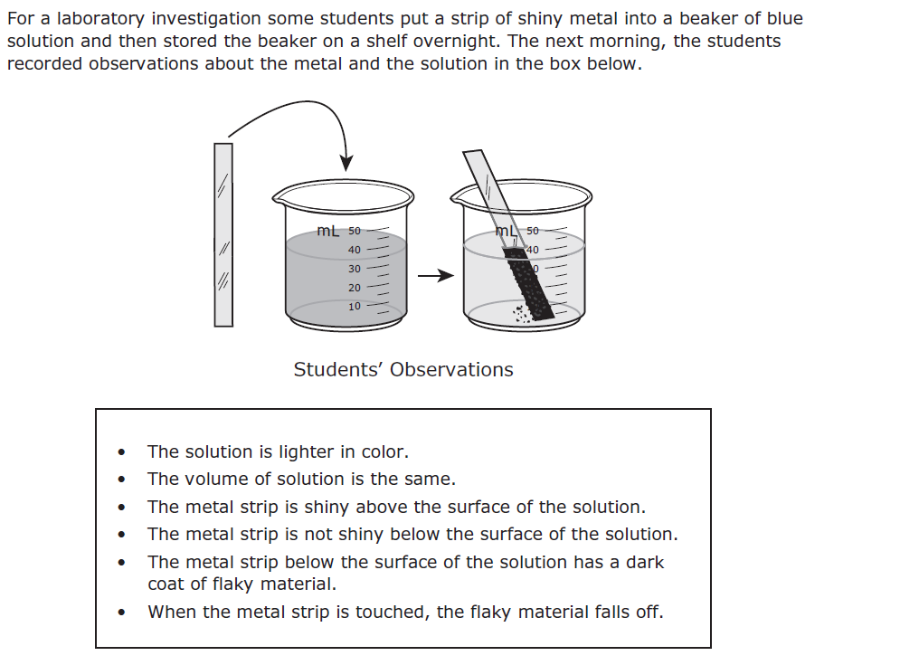
Ch103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis And Cellular Function Chemistry




General Chemistry Chemistry




Science Test Over Chapters 4 7 Flashcards Quizlet




Pdf A Purely Green Synthesis Of Silver Nanoparticles Using Carica Papaya Manihot Esculenta And Morinda Citrifolia Synthesis And Antibacterial Evaluations



Www Aocs Org Documents Informpdf Inform september 18 4 Pdf



Www Lcsnc Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid Dataid Filename Ap chem student lab manual Pdf



Print Staar Released Test Eight Grade Flashcards Easy Notecards



Lab 4 Chemical And Physical Changes




Papermaking Vol 5 No 1 19 By Pita Co Uk Issuu




In A Previous Experiment A Green Crystalline Product Having The



Www Pearson Com Content Dam One Dot Com One Dot Com International Schools Pdfs Secondary Curriculum International Gcse Science International Gcse Chemistry Student Book Sample Pdf
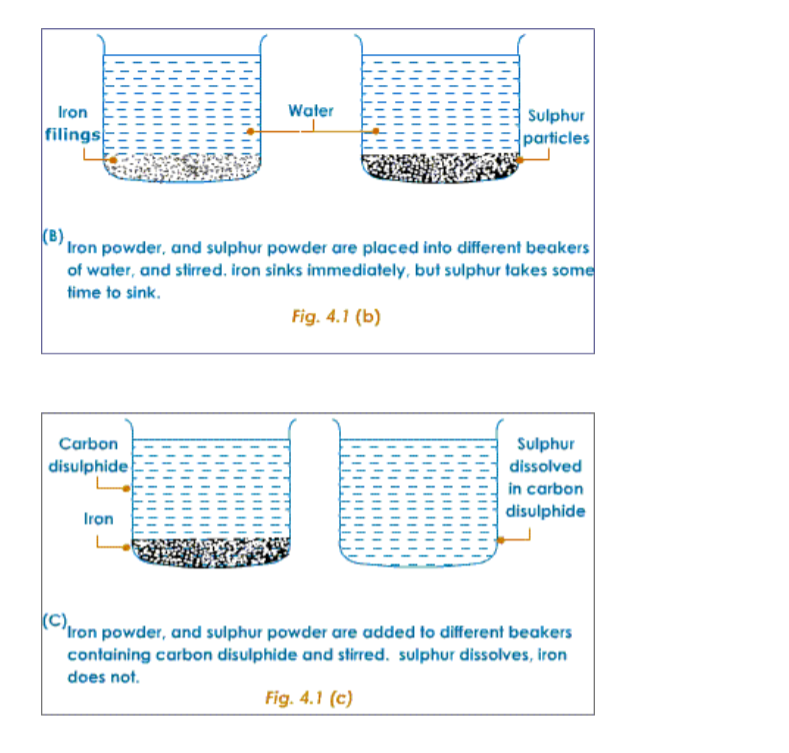



Chemistry Notes Form 1 Chemistry Form One Pdf Online Notes Chem




Convection Heat Energy Transfer Siyavula




Laboratory Manual Table Of Contents Experiments




Gummy Bear Science Project Diy For Beginners Kiwico




Standard Santee Education Complex




Heat Temperature And Conduction Chapter 2 States Of Matter Middle School Chemistry



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿